What PV Manufacturers Need to Know
The United States is currently experiencing unprecedented growth in solar energy usage due to a number of factors, including government subsidies, mandates to utilities, robust technology improvements, lower silicon production costs, and uncertainties surrounding fossil fuel production. Indeed, 2016 was a bright spot for the US market, where solar energy ranked as the number one source of new electric generating capacity additions. Altogether, solar power last year accounted for 39 percent of new capacity additions across all fuel types.
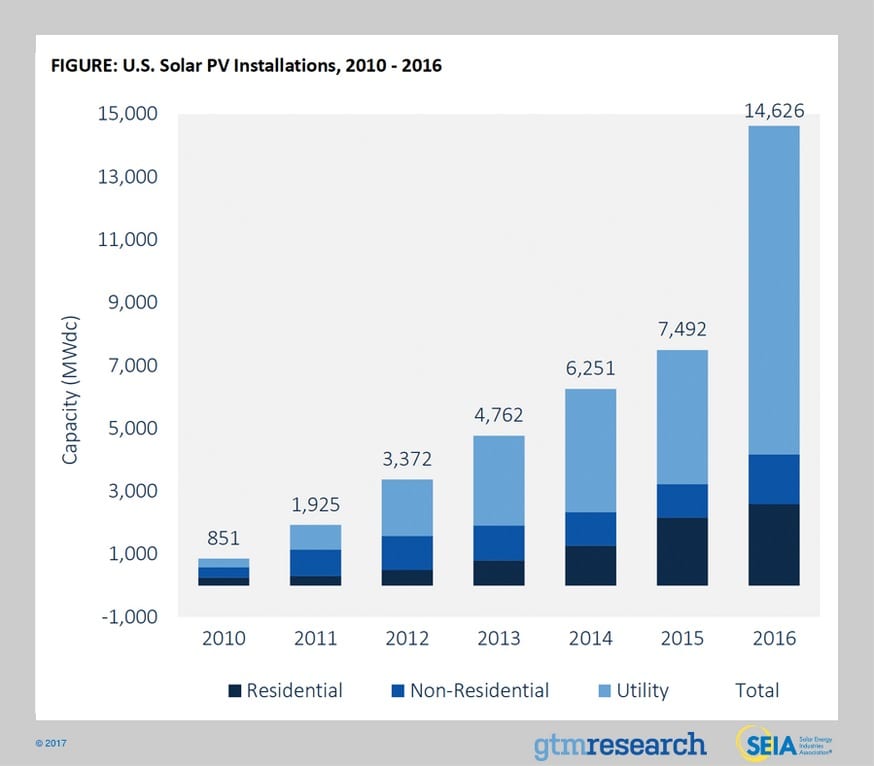
According to the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA) and market analysis firm GTM Research, 2016 was the US solar market’s biggest year to date, with 14,626 megawatts (MW) of solar photovoltaic (PV) installed, as shown in the table below.
Growing Demand from the Utility Scale Segment
Last year’s growth year was driven largely by the utility-scale segment. Supported by a range of solar projects initially hedging against the extension of the federal Investment Tax Credit, the utility-scale segment featured the highest growth rate of any segment, growing 145 percent over 2015. “While U.S. solar grew across all segments, what stands out is the double digit gigawatt boom in utility-scale solar, primarily due to solar’s cost competitiveness with natural gas alternatives.”, explains Cory Honeyman, GTM Research’s associate director of U.S. solar research. As a result of a remarkable 2016, the U.S. is now home to more than 1.3 million solar PV installations with a cumulative capacity of over 40 gigawatts.
Data from SEIA’s annual Solar Means Business report show that major U.S. corporations, including Target, Walmart and Apple are going solar at an incredible rate. The top 25 corporate solar users in America had installed nearly 1,100 MW of capacity at 2,000 different facilities across the country as of October 2016.
Lower Costs Throughout the PV Supply Chain
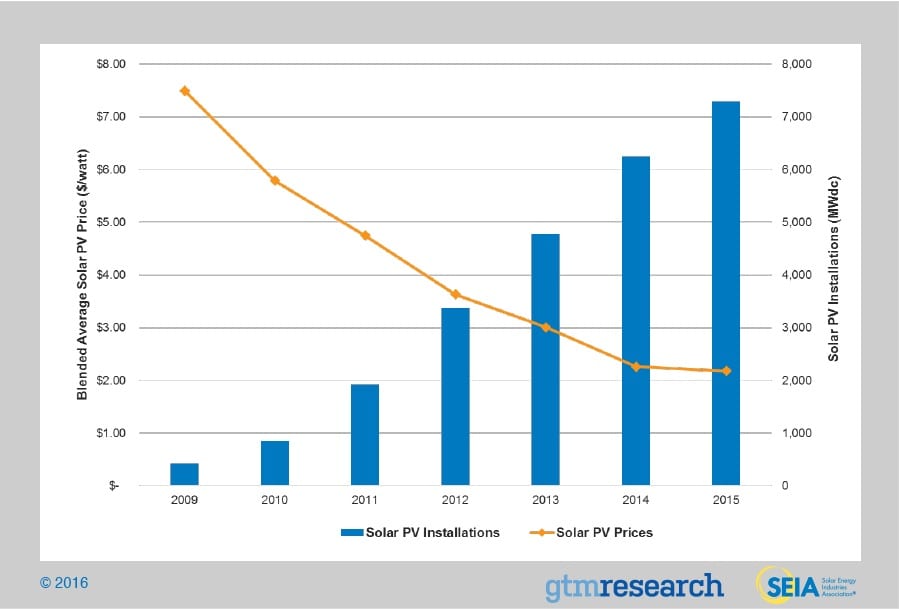
The cost to install solar has dropped by more than 60% over the last 10 years, leading the industry to expand into new markets and deploy thousands of systems nationwide. These lower costs are the result of the declining prices of raw materials used by PV manufacturers, as well as lower soft costs, including labor, supply chain and overhead considerations. In terms of the American market, the U.S. Department of Energy is working to help alleviate soft costs, collaborating with cities and counties across the country to streamline permitting processes and reduce local barriers to going solar.
Photovoltaics Technology Costs Today
The cost of PV has dropped dramatically as the industry has scaled up manufacturing and incrementally improved the technology with new materials. Installation costs have come down too with more experienced and trained installers. Most modern solar cells are made from either crystalline silicon or thin-film semiconductor material. Silicon cells are more efficient at converting sunlight to electricity, but generally have higher manufacturing costs. Thin-film materials typically have lower efficiencies, but can be simpler and less costly to manufacture.
Article by: Olivier Benny